The healthy secret of the Japanese
5 Key Nutrients of Japanese Green Tea
Why is Japanese green tea known to be such a healthy drink? The secret lies in the nutrients it contains. Recent studies have unveiled and proven the amazing health benefits of Japanese green tea.
First let's take a quick glance into some of the key nutrients and how they have positive effects to your body.
- Catechin
- Theanine and other Amino Acids
- Vitamin C
- Fluorine
- Potassium and other Minerals
*we'll also talk about Caffeine.
5 key nutrients of Green Tea - a quick summary

Catechin
Perhaps Catechin is the main health nutrient when it comes to green tea.
Catechins are a type of polyphenol and is the astringency component in green tea. The number one benefit of this nutrient is perhaps its powerful anti-oxidation and anti-aging effect. In short, it keeps you young and strong!
It does so by restraining the "free radicals" produced in your body from attacking the cells of your body. This attack is the base mechanism behind the aging of your cells, and is the root cause of any type of illnesses.
With Catechin, the activity of the free radicals will be contained, and will prevent your cells from aging. This will help in boosting the immune system to keep you away from all illnesses.
While Vitamins such as Vitamin C and Vitamin E also have anti-oxidation effects, Catechins can contain up to ten times - or even higher levels of anti-oxidation effects.
This is why drinking green tea on a daily basis is viewed as an extremely important and healthy habit!
Some of the other effects of Catechin include reducing body fat, reducing blood cholesterol, inhibits high blood pressure, bad breath prevention, and prevents tooth decay. WOW, that's a lot!!
As you can see, Catechin is indeed a magical nutrient - and Japanese green tea is loaded with it. While other the such as black tea or oolong tea use the same tea leaf as Japanese green tea, there is actually a huge difference in the amount of Catechin the Japanese green tea contains.
The Catechin in tea leaves are very easily oxidized. This means that the levels of Catechin will significantly decrease during the oxidation that takes place for black tea or oolong tea. However, Japanese green tea leaves are steamed immediately after harvesting to stop this oxidation, allowing the Catechin to remain in the leaves at high levels. This is why the Japanese green tea is considered much more healthy than other types of tea.
Theanine (and other Amino Acids)
Theanine is the full-bodied, umami flavour component of green tea.
It is a type of amino acid, and it constitutes more than half of the types of amino acid in the Japanese green tea. Other types of amino acid contained in Japanese green tea include Glutamic Acid, Aspartic Acid, Arginine, and Serine.
Theanine is also an incredibly powerful nutrient! Its health benefits include lowering blood pressure, relaxation, and helps improve memory and learning.
One thing to additionally note is the effect it has on the Caffeine substance contained in the Japanese green tea. While caffeine has a stimulation effect to the body, Theanine actually works to reduce that effect. Therefore, the caffeine taken through Japanese green tea is said to be much healthier than other caffeine drinks such as coffee. This is one of the reasons health experts recommend Japanese green tea over coffee.
Now let's look at this chart below, which shows the amount of Catechin and Theanine which each type of infused Japanese Green Tea may contain.
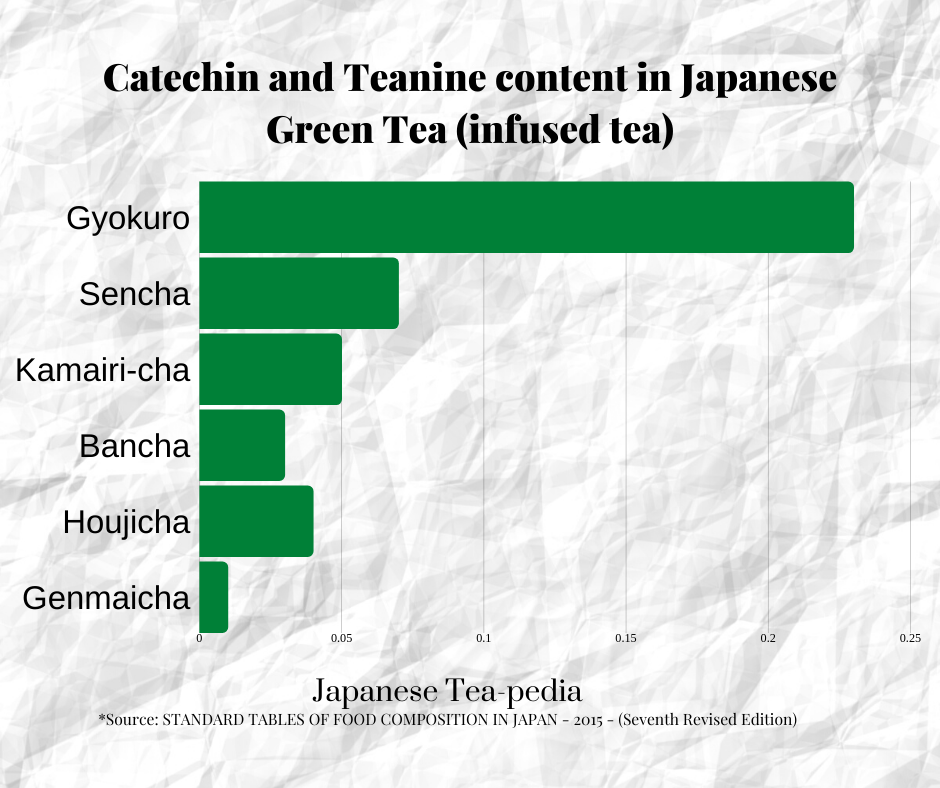
Gyokuro, by far, contains the most amount of Catechin and Theanine among the Japanese teas, at 0.25 grams per 100 ml. Sencha and Kamairi-cha follows. So if you're really looking for these nutrients, Gyokuro will be the choice out of the infused teas.
- Firstly, gyokuro would generally use higher quality leaves than others, and the higher quality leaves will contain higher levels of nutrients.
- Also the preparation would be a little different. It requires a higher usage of tea leaves to hot water, and also a longer seeping period.
Matcha is not in this chart as it is not prepared through infusion. However, it will contain significantly higher amounts even compared to Gyokuro, as Matcha allows for direct consumption of the tea powders.
Vitamin C (and other Vitamins)
Vitamin C's health benefits are well known. It is one of the most important nutrients for your body.
- First of all, Vitamin C, by its own right, is a great antioxidant as well. It helps keeps the body and cells younger, and boost the overall immune system. In green tea you can benefit from the double effect of catechin and Vitamin C to fend off free radicals.
- It also helps to maintain your skin healthy and beautiful as Vitamin C functions to build collagen and iron levels in your body.
- It also lowers your blood pressure as it helps remove the sodium from the body.
Aside from these, what's not as well known about the Vitamin C in green tea is how the Catechin is able to compliment it. Chatechin helps the absorption of vitamin C into the body. Although Vitamin C tends to be easily destroyed by heat, the Catechin protects that from happening.
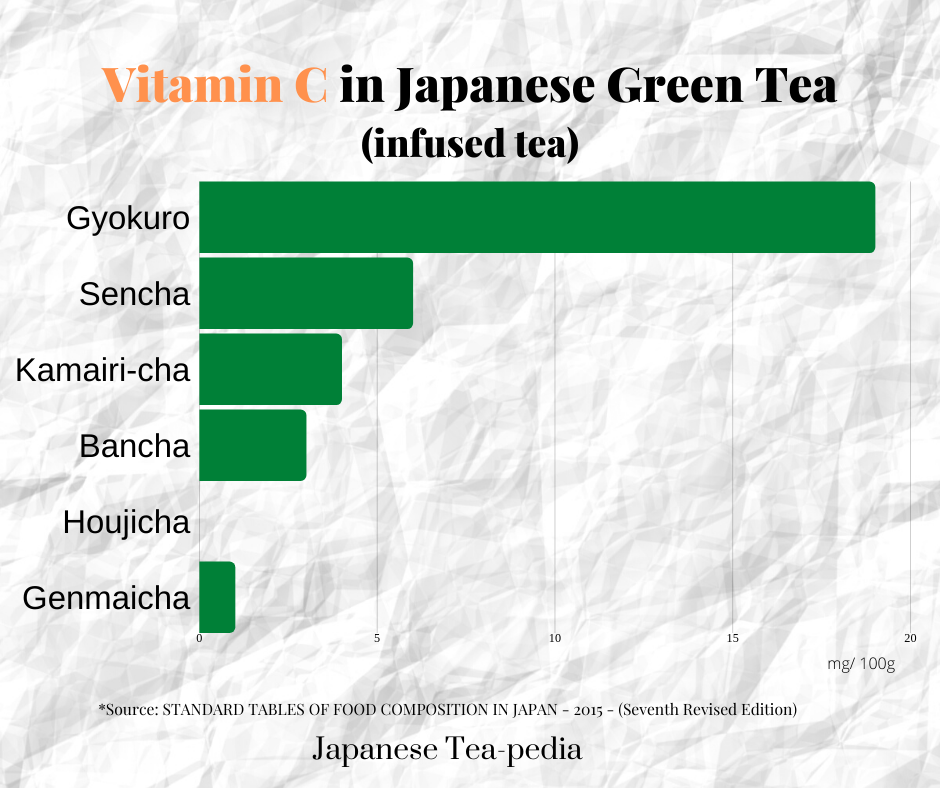
Here below are the differences of the Vitamin C levels for each type of Japanese green tea. Similar to catechin and theanine, gyokuro contains the highest amounts.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the bitterness component of green tea. As is has a stimulation effect, it is not always regarded as a "health nutrient". However, taken properly it has health benefits as well. Benefits coming from Caffeine include the following.
- increasing alertness
- increasing stamina
- acts as a mild diuretic, or increases the passing of urine
- Prevention of hangover
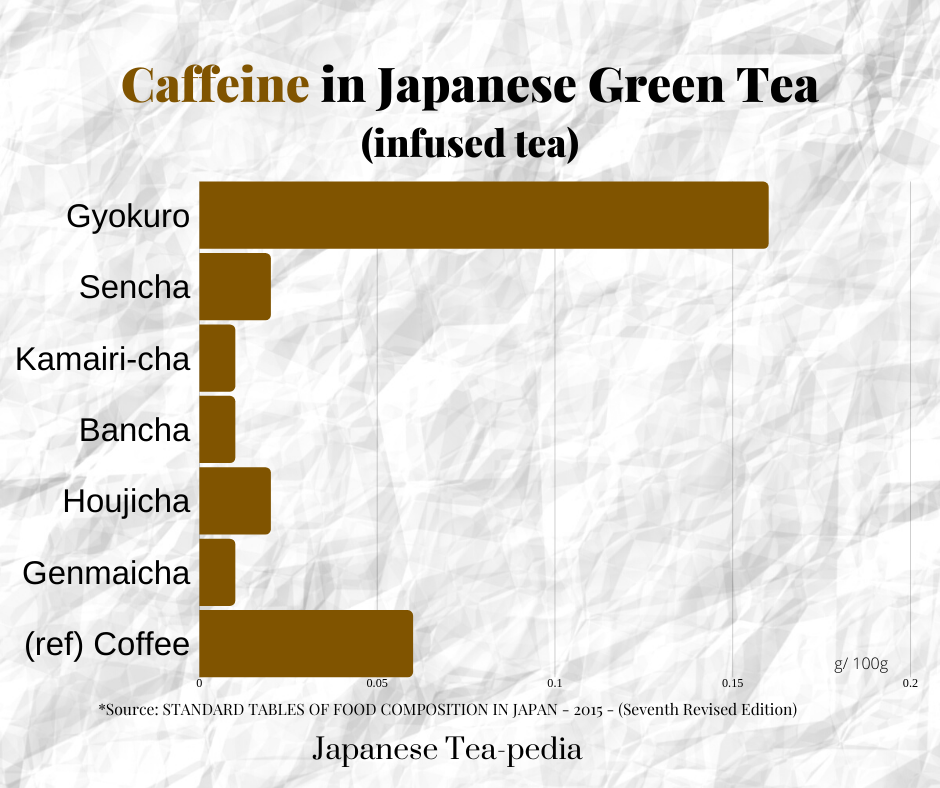
As mentioned in the Theanine sectinon, the caffeine in Japanese green tea is much healthier than other caffeine drinks as the Theanine reduces the stimulation effect of the caffeine.However, especially for gyokuro, you may want to control the intake as it has much higher levels of caffeine even compared to coffee.As you can see in the chart below, the other green teas are significantly lower than Coffee.
Fluorine
The flourine contained in Japanese green tea is said to strengthen your teeth and prevent tooth decay.
There are actual studies conducted with kids in Japan which proved that a regular habit of drinking green tea reduced the number of cavities for kids.
Potassium and other Minerals (Calcium, Manganese, Phosphorous, etc.)
Japanese green tea contains many minerals as well - it is especially loaded with Potassium.
Potassium has great health benefits as it helps to remove the excess sodium in the body. This is important for people with high BP, as it helps to reduce the high blood pressure.
It is also said to prevent strokes and reduce other heart diseases.
It's also good for kids as it is said to help prevent Osteoporosis - which is a condition where the bones become hollow and weak. This is because potassium helps retain the calcium in the body.
Summary
Do all Japanese green tea contain these nutrients? The answer is YES, they do.
Although the amount may differ depending on the tea, they all contain these nutrients to a certain extent.
If you're really shooting for nutrients, perhaps the best may be matcha, as you can consume the leaf powder and absorb 100% of the nutrients. You can also try using used gyokuro leaves for cooking as well.
"Shincha", or the teas from leaves from the first harvest of the year will also be high in nutrients.
These are some considerations, but the bottom line is, all Japanese green tea are really healthy drinks. Find a few you like, and enjoy everyday to carry out your healthy lifestyle.
